Bluebonnets and the Texas Legislature Exhibit

Every spring, Texas fields and roadsides burst into a sea of blue blossoms. This beautiful display is thanks to the Lupinus, or bluebonnet, a wildflower species native to Texas. The flower’s common name comes from the shape of its petals, which resemble the bonnets colonial women wore to protect themselves from the Texas sun. All species of bluebonnet are collectively the State Flower of Texas.
To honor the state flower, the Legislative Reference Library has created the Bluebonnets and the Texas Legislature exhibit. The items in the Library’s display cases below highlight bluebonnet-related legislation passed by the Texas Legislature, along with artwork, songs, stories, and artifacts inspired by the flower.
Bluebonnets and the Texas Legislature:


Selecting a State Flower: Bluebonnet, Cotton, or Cactus?
In 1901, at the request of the National Society of Colonial Dames of America in Texas, the Texas Legislature adopted the Lupinus subcarnosus, better known as the bluebonnet, as the official state flower. Senate Concurrent Resolution (SCR) 10, 27th Regular Session (R.S.), authored by Senator Philip Barry Miller, was introduced in the Senate chamber on February 28. The House Journal from the same day reports a "Message From The Senate" that the Senate passed SCR 10.

Senator Philip Barry Miller
The next step in the legislative process requires the opposite chamber to consider the resolution and decide whether to amend and send it back, pass it as written, or not pass it at all.
The Texas House of Representatives took up SCR 10 on March 4. During the debate, Representative Philip Hathaway "Phil" Clements offered an amendment proposing the cotton boll as an alternative, poetically describing it as "the white flower of commerce." Representative John Nance "Cactus Jack" Garner offered a substitute to the amendment proposing that the flower of the prickly pear cactus be the state flower.

Representative Philip Hathaway "Phil" Clements

Representative John Nance "Cactus Jack" Garner
Representative Garner's substitute was quickly tabled. The House Journal does not provide much context, but his proposal for the cactus earned him the nickname "Cactus Jack."
Representative William Winston Dillard offered an amendment to Representative Clements' amendment to use the word "bloom" instead of "boll." They ran out of time to consider the amendment, so it was put on hold. The following day, on March 5, Representative Dillard withdrew his "bloom" amendment.
Representative Clements' cotton boll amendment was popular, but the Colonial Dames staged an all-out show of support for the bluebonnet that ultimately carried the day. In addition to putting bluebonnet bouquets on each legislator's desk, the Dames borrowed a large oil painting of the blossoms by Austin artist Mode Walker and carried it onto the floor of the Legislature to give members a visual reminder of their beauty. The House voted against Representative Clements' amendment, and the resolution as written by the Senate was adopted.

Bluebonnets and Evening Primroses, Mode Walker, c. 1900, oil on canvas.
The original work is in the permanent collection of the Neill-Cochran House Museum and currently hangs in their front hall.
The House and Senate Journals are records of activity that occurs on the House or Senate floors, but they do not record every detail of what occurs in the legislative chambers. Historical newspapers from 1901 can provide more information, like the following excerpt that explains why Representative Clements changed his mind from the cotton boll to the "blue bonnet."

Texas' Flower (excerpt), Caldwell News-Chronicle, March 15, 1901, University of North Texas Libraries, The Portal to Texas History, crediting Harrie P. Woodson Memorial Library.
To see the journal pages and some news coverage from 1901 about the passing of this legislation go to Additional Resources.
Elizabeth M. D. Welch, the President of the National Society of Colonial Dames of America in Texas, sent letters to both the House and the Senate to share the Dames' gratitude for the passage of the concurrent resolution making the "blue bonnet" the official state flower. The House read and recorded their letter in the House Journal on March 7. The Senate read and recorded their letter in their Journal on March 8.
Governor Joseph Draper Sayers signed SCR 10 on March 7, 1901. The original signed copy of the resolution is housed in the Texas Secretary of State collection at the Texas State Library and Archives Commission.

Senate Concurrent Resolution 10, 27th Legislature, Regular Session (1901), Texas Secretary of State legislative bills and resolutions filed, Courtesy of Texas State Library and Archives Commission.
Adding More Bluebonnets
SCR 10, 27th R.S., designated only the
Lupinus subcarnosus as the state flower, but there are several bluebonnet species in Texas, including the
Lupinus texensis and the
Lupinus harvardii or “Big Bend” bluebonnet. In 1971, the Texas Legislature adopted
HCR 44, 62nd R.S., to include the
Lupinus texensis and all other varieties of bluebonnet as the official state flower. Representative
Aubry Lee Moore was the author and Senator
James Powell "J.P." Word sponsored the concurrent resolution in the Senate.
Top
Is It Illegal to Pick Bluebonnets?
There is a common belief among Texans that picking bluebonnets is illegal. Despite what you may have heard, there currently is no specific state law prohibiting the picking of bluebonnets.
HB 47, 43rd R.S. (1933), authored by Representative Robert Emmett Morse, made it unlawful to pick "any tree, shrub, vine, flower or moss" on certain lands without permission. This language was included in Title 17, Art. 1388a of the Penal Code. The law specifically mentions bluebonnets, Indian paint brushes, and other wildflowers under prohibitions against transporting or selling flowers gathered in violation of the law.
SB 34, 63rd R.S. (1973), adopted a new Penal Code through a substantive revision process. Several articles, including Art. 1388a, were repealed.
Keep in mind, there are laws against trespassing and damaging government property.
Top
Official State Flower Song—"Bluebonnets"
In 1932, Lora C. Crockett and Julia D. Booth wrote the song "Bluebonnets." Crockett composed the music and Booth wrote the lyrics.
On February 8, 1933, Representative Robert A. Fuchs introduced soprano Alice Clay Routt and pianist-composer Lora C. Crockett to the Texas House of Representatives chamber to perform "Bluebonnets."
The following week, on February 16, Representatives Fuchs and John Manson Mathis, Sr. introduced HCR 24, 43rd R.S. (1933), which proposed the adoption of "Bluebonnets" as the Texas State Flower Song. The House passed it the same day. The Senate adopted the concurrent resolution on March 13. Governor Miriam Ferguson signed the resolution on March 21, 1933.
A reproduction of the sheet music appears below along with a recording of the song.
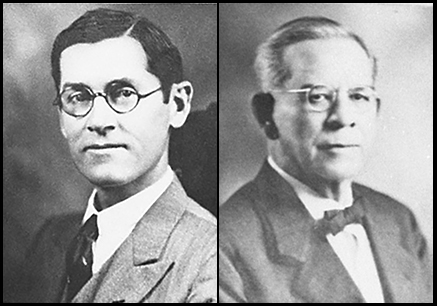
Representative Robert A. Fuchs and Representative John Manson Mathis, Sr.
Recording of Bluebonnets Song
Bluebonnets song performed by Donald Brower on piano.
Bluebonnets Sheet Music

Bluebonnets, music by Lora Coston Crockett, lyrics by Julia D. Booth
When the pastures are green in the springtime
And the birds are singing their sonnets,
You may look to the hills and the valleys
And they're covered with lovely Bluebonnets.
Blue is the emblem of loyalty,
They're as blue as the deep, deep sea,
Their smiling faces bring gladness,
For they bloom for you and for me.
Bluebonnets, so gorgeous and stately,
In your mantle of blue and of green,
In the spring when you're in your full glory,
You're the loveliest sight ever seen.
You're beautiful when you sway in the sunshine,
You look like waves of the sea,
Ah, Texas was wise in her choice of a flower,
So we offer our homage to thee.
CHORUS
Bluebonnets, blue lovely Bluebonnets,
More beautiful than all the rest.
Texas chose you for her flower,
And we love you best, Bluebonnets.
Top
Official State Tartan—"Texas Bluebonnet Tartan"
June McRoberts of Salado was inspired by the bluebonnet to design a tartan with colors representing Texas' state flower. She registered the Texas Bluebonnet tartan with the Scottish Tartans Authority in 1985.
The Texas Bluebonnet Tartan was selected to serve as the 1986 Sesquicentennial Texas Tartan, and a scarf of its design was presented to then-Governor Mark W. White, Jr. at the crowning of the Texas Bluebonnet Queen.
In 1989, the Texas Legislature passed HCR 242, 71st R.S., which recognized the Texas Bluebonnet Tartan as the Official Tartan of Texas. Representative Stanley "Stan" David Schlueter authored the resolution and Senator John Nesbett Leedom was the sponsor. The resolution passed the House on May 19 and the Senate on May 25. It was signed by Governor William P. Clements on May 29, 1989.
The resolution noted that "many Texans of Scottish descent continue to carry on the proud traditions of their forbears" and acknowledged that "people of Scottish descent played a major role in the settlement and development of Texas."

The Texas Bluebonnet Tartan, The Scottish Register of Tartans, National Records of Scotland.
Top
Art, Stories, Songs, and Artifacts Inspired by Bluebonnets
Hattie V. Palmer, South Texas' Ranking Painter of Bluebonnets
Artist Hattie Virginia Palmer (1866–1933) may not have been Texan by birth, but her legacy celebrates one of the iconic images of her adopted state—fields of Texas bluebonnets.
Born Hattie Virginia Young in Ripley, Ohio, on May 29, 1866, Palmer studied drawing and china painting at the Cincinnati Academy of Art from 1894–1897. In 1902, she married Charles Palmer, and the two settled in Houston, Texas in 1907. Palmer became active in the state’s art scene as a member of the Texas Fine Arts Association, the Southern States Art League, and as a founding member of the Houston Art League, which later became the Museum of Fine Arts.
Palmer was captivated by the fields of blue wildflowers that bloom every spring across the state. Among her best-known paintings are "Texas Bluebonnets" and "Misty Morning of Spring," and her images of the state flower earned her the distinction of "South Texas' Ranking Painter of Bluebonnets" in 1924.
In 1924, Palmer showed her work at a one-woman exhibition at Houston's Museum of Fine Arts. Over her career, her work was also included in exhibitions in Wichita Falls, Fort Worth, and Austin, as well as in Ohio, Indiana, and Tennessee. She died in Houston, her adopted home, on October 11, 1933.
She often signed her paintings H. V. Palmer.
Source: An Encyclopedia of Women Artists of the American West, Phil Kovinick and Marian Yoshiki-Kovinick, 1998.
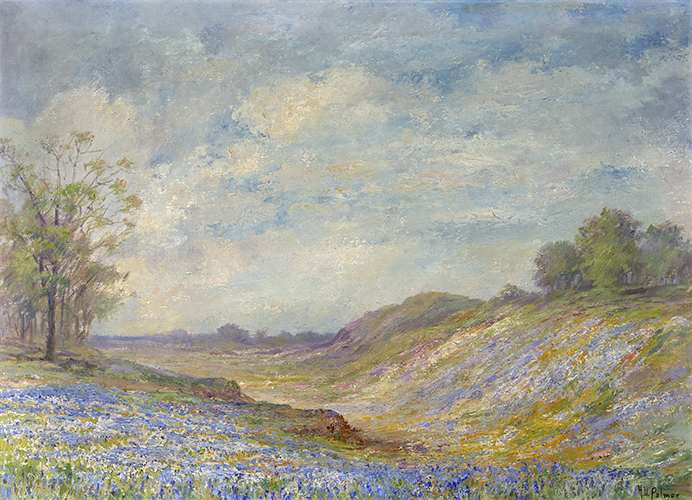 Image courtesy of private collector.
Image courtesy of private collector.
Stories and Legends
There are many stories and legends about the bluebonnet flower. Some are related to the origin and the symbolism surrounding the state flower. The Library's collection includes some books and memorabilia.
 Legend of the Bluebonnet: An Old Tale of Texas
Legend of the Bluebonnet: An Old Tale of Texas, by Tomie dePaola
This is the story of a young Comanche girl, She-Who-Is-Alone, whose tribe is suffering through a drought and famine. The tribe dances to the Great Spirits for rain and the shaman says that a burnt offering of the most valued possession among the tribe is needed.
She-Who-Is-Alone sacrifices her beloved doll, a gift from her deceased mother, as an offering. The Great Spirits reward her selflessness not only with the rain that saves the tribe, but with fields of beautiful bluebonnets.
Miss Lady Bird’s Wildflowers: How a First Lady Changed America, by Kathi Appelt and Joy Fisher Hein
Tells the true story of former First Lady Claudia "Lady Bird" Johnson’s life and her environmental efforts. Lady Bird lost her mother at a very young age. As a child, she was told a story of when her mother greeted Lady Bird's father with a bouquet of bluebonnets. Lady Bird was so moved by this account that every time she saw a bluebonnet she was comforted and felt loved.
As the First Lady, her love of flowers and nature were instrumental in the passage of the federal
Highway Beautification Act in 1965, which led to the planting of native wildflower seeds along the highways of Texas. She also established the
Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center located southwest of Austin.
Today, the Texas Department of Transportation buys and sows about 30,000 pounds of wildflower seeds every year through its
Wildflower Program.
The Legend of the Pink Bluebonnet, Aggie Horticulture, Texas A&M University
A legend collected by Greg Grant tells of two children near San Antonio who discovered one white and one pink bluebonnet growing amidst a field of blue ones. Their grandmother told them that the white flower was said to represent the lone star on the Texas flag and the pink grew in memory of those who gave their lives at the battle of the Alamo.
The Legend of the Bluebonnet, "Dolls of Legends" series, by Texas artist
Thacker Cole
Thacker Cole was told a bluebonnet story as a young girl, and she created this doll to go along with it. The story tells of how men sent to search for water during a severe drought thought they saw a little girl in a white dress and blue bonnet near a burned-out wagon train. When they tried to find her, they found the bonnet on the ground with a beautiful blue flower growing beneath it. At that moment, it began to rain—and soon the entire field was filled with flowers. The men named the flower for the little girl's blue bonnet, whose owner was never discovered.
 Doll and booklet donated to the Legislative Reference Library by Donna Farley of Hallsville, Texas.
Doll and booklet donated to the Legislative Reference Library by Donna Farley of Hallsville, Texas.
Songs Inspired by Bluebonnets
The blue blossoms have inspired musical works in addition to the State Flower Song. In 1936, the state held a
Centennial Exposition to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the establishment of the Republic of Texas. The Exposition featured a variety of musical events, showcasing music written not just by professional composers but by amateurs as well. The Texas Federation of Music Clubs (TFMC), a major organizer for the Exposition, appointed a special committee to select music "appropriate for Centennial use," and many of its members submitted songs featuring Texas themes—including bluebonnets. The pieces of sheet music on display here at the library, by TFMC members Camilla Hendrix and Ida Bassett Botts, represent just two of the dozens of bluebonnet songs written for Centennial celebrations.
Legend of the Bluebonnets, Words and music by Ida Bassett Botts. Performed by Elizabeth Bellisario on violin.
Texas Bluebonnet Waltz, Words and music by Camilla Hendrix. Performed by Elizabeth Bellisario on violin.
 Texas Composers Collection, Dolph Briscoe Center for American History, The University of Texas at Austin.
Texas Composers Collection, Dolph Briscoe Center for American History, The University of Texas at Austin.
Bluebonnet Artifacts
Bluebonnets have adorned many artifacts and objects since 1901, including those commemorating special events in Texas history. They are iconic and beloved imagery for Texans and can be seen on historical and contemporary pieces. Below are just a few items that are special to the Capitol and Texas' major anniversaries.
Tea Cup
This is a Sheraton-shape dual-handled tea cup from a 45-piece set of this china pattern. The
State Preservation Board (SPB) has a 75-piece set of the Bluebonnet China pattern, which has been on display in the Speaker’s apartment at various times. The SPB’s set was “purchased as a wedding gift from the Kooch Company, a store then located on South Congress Avenue in Austin.”
 Texas Bluebonnet Tea Cup.
Texas Bluebonnet Tea Cup. W. H. Grindley & Co., Ltd., England. c. 1928. Porcelain.
On loan from the private collection of Hugh L. Brady, House Parliamentarian.
Vase
This piece commemorates the 1936 Texas Centennial, the 100th anniversary of the establishment of the Republic of Texas. The company made several bluebonnet items for the Texas Centennial, including trinket boxes, small bowls and trays, and ashtrays.
 Texas Bluebonnet Vase.
Texas Bluebonnet Vase. Tashiro Shoten Ltd., Japan. c. 1936. Porcelain.
On loan from the private collection of Hugh L. Brady, House Parliamentarian.
Tea Cup
The following tea cup was created as part of a series featuring the official flowers of the 48 states. The source of the verse is unknown, but it does not match the lyrics of the official state flower song, “Bluebonnets” by Laura D. Booth and Lora C. Crockett.
 Texas Bluebonnet Tea Cup.
Texas Bluebonnet Tea Cup. J.W. Webster, England. c. 1956. Porcelain.
On loan from the private collection of Hugh L. Brady, House Parliamentarian.
Cup Plate
The embossed glass cup plate was issued to commemorate the 1986 Texas Sesquicentennial celebrating the 150th anniversary of the establishment of the Republic of Texas. It was commissioned by Deer Trail Designs, Dallas and designed by Rachel Garland, also of Dallas.
 Texas Bluebonnet Cup Plate.
Texas Bluebonnet Cup Plate. Pairpoint Glass Co., Massachusetts, c. 1986. Pressed glass.
On loan from the private collection of Hugh L. Brady, House Parliamentarian.
Pin Tray
This jasperware pin tray commemorates the 1986 Texas Sesquicentennial and was commissioned by the Ivy House, Dallas. In addition to the pin tray, other commissioned items included a paperweight, trinket box, and pen tray, all adorned with the Texas state seal.
 Texas Bluebonnet Pin Tray.
Texas Bluebonnet Pin Tray. Josiah Wedgwood & Sons, Ltd., England. c. 1986. Jasperware.
On loan from the private collection of Hugh L. Brady, House Parliamentarian.
Barbed Wire Bluebonnets
These five handmade bluebonnet flowers create a unique bouquet that ties two symbols of Texas together: the barbed wire and the bluebonnet. They are placed throughout the display in the library, but are shown below as a group.
 Bluebonnets with Barbed Wire Stems.
Bluebonnets with Barbed Wire Stems. Frances Henry, Mansfield, Texas. Modeling clay and barbed wire.
Donated to the Legislative Reference Library by the artist.
Top
Bluebonnet-Related Legislation
| YEAR |
BILL |
SESSION |
HOW IT RELATES |
| 1901 |
SCR 10 |
27th R.S. |
Adopting a state flower. |
| 1903 |
SB 147 |
28th R.S. |
Relating to protecting the public grounds of the State of Texas. |
| 1933 |
HCR 24 |
43rd R.S. |
Providing for the adoption of a State Flower Song. |
| 1933 |
HB 47 |
43rd R.S. |
Prohibiting the wilful taking, injury, or destruction of trees, shrubs, vines, flowers, and moss on certain lands. |
| 1971 |
HCR 44 |
62nd R.S. |
Designating the Lupinus texensis and any other variety of bluebonnet not heretofore recorded as the official state flower of Texas. |
| 1973 |
SB 34 |
63rd R.S. |
Reforming the Penal Law; enacting a new Penal Code . . .
Section 3a of this bill repealed V.T.P.C. Art. 1388a, which was enacted by HB 47, 43rd R.S. (1933). This article addressed the picking of bluebonnets. |
| 1981 |
SCR 108 |
67th R.S. |
Recognizing Burnet and Llano counties as the Bluebonnet Co-Capitals of Texas. |
| 1989 |
HCR 242 |
71st R.S. |
Recognizing the Texas Bluebonnet Tartan as the Official Tartan of Texas. |
R.S. = Regular Session
HB = House Bill
SB = Senate Bill
HCR = House Concurrent Resolution
SCR = Senate Concurrent Resolution
Top
Additional Resources
- About John Nance Garner, Briscoe Center for American History
- "Cactus Jack" Garner, Folklore: in All of Us, in All We Do, The Portal to Texas History, University of North Texas Libraries, crediting UNT Press
- Color-ization of the State Flower, Aggie Horticulture, Texas A&M University
- DPS Offers Safety Tips for Enjoying Texas Wildflowers, Texas Department of Public Safety, April 9, 2015
- The Legislative Process in Texas, Texas Legislative Council, 2023
- Lupinus texensis, Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center
- Texas Centennial 1936: Music and Identity, Kevin E. Mooney, The University of Texas at Austin ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 1998
- Texas Centennial Music, Handbook of Texas
- Texas Sesquicentennial Guide to Events, 1986, Texas 1986 Sesquicentennial Commission, 1986, LRL Collection, S800.5 G941
Additional Resources Related to SCR 10, 27th R.S. (1901)—Adopting a State Flower
House & Senate Journals, Legislative Reference Library of Texas
- February 28, Senate Journal, SCR 10 introduced
- February 28, House Journal, Message from the Senate that SCR 10 passed
- March 4, House Journal, SCR 10 laid before the House; Rep. Clements offered his cotton boll amendment and Rep. Garner offered his cactus amendment
- March 5, House Journal, Resolutions, SCR adopted
- March 6, House Journal, Signed by the Speaker
- March 7, Senate Journal, Committee on Enrolled Bills
- March 7, House Journal, Dames' thank you letter read to the House
- March 8, Senate Journal, Dames' thank you letter read to the Senate
Historical Newspapers, The Portal to Texas History, University of North Texas Libraries
- The legislature has at length . . ., Bryan Morning Eagle, March 7, 1901
- Blue Bonnet or Buffalo Clover Adopted as the State Flower of Texas, The Democrat, March 7, 1901, crediting Collin County Genealogical Society
- The House was unable . . ., The Weekly Herald, March 7, 1901
- Buffalo Clover Designated as Emblematic Flower, Alpine Avalanche, March 8, 1901, crediting Bryan Wildenthal Memorial Library (Archives of the Big Bend)
- Blue Bonnet or Buffalo Clover Adopted as the State Flower of Texas, Meridian, March 8, 1901, crediting Meridian Public Library
- Says the Austin correspondent . . ., The Bastrop Advertiser, March 9, 1901, crediting Bastrop Public Library
- Texas' Flower, Caldwell News-Chronicle, March 15, 1901, crediting Harrie P. Woodson Memorial Library
Additional Resources Related to HCR 24, 43rd R.S. (1933)—Providing for the adoption of a State Flower Song
House & Senate Journals, Legislative Reference Library of Texas
- February 8, House Journal, Song performed in the House
- February 16, House Journal, HCR 24 introduced and adopted
- February 16, Senate Journal, Message from the House that they passed HCR 24
- March 8, Senate Journal, Reported out favorably by the committee
- March 13, Senate Journal, Read and adopted by Senate
- March 13, House Journal, HCR 24 passed and returned from the Senate
- March 20, House Journal, HCR 24 signed by the Speaker
- March 21, Senate Journal, HCR 24 signed by the Lieutenant Governor
Historical Newspapers, The Portal to Texas History, University of North Texas Libraries
- "Bluebonnets" Be Sung Before the Legislature, Brenham Banner-Press, February 6, 1933, crediting Nancy Carol Roberts Memorial Library
- Mrs. Mark Coston . . ., Brenham Banner-Press, February 10, 1933, crediting Nancy Carol Roberts Memorial Library
- "Bluebonnets" Is Voted by House as State Flower Song, Brenham Banner-Press, February 17, 1933, crediting Nancy Carol Roberts Memorial Library
If you have any questions or would like to know how to find additional legislative resources, please call us at (512) 463-1252 or email us at
LRL.Service@lrl.texas.gov.
Unless otherwise noted, photos courtesy of the Texas State Preservation Board or Legislative Reference Library staff.
This entry was posted on June 12, 2024 at 3:30 PM and has received 4864 views.
Print this entry.
































































